Configure a Spring Boot app for HTTPS on Amazon AWS.
Even trivial websites are moving from HTTP to HTTPS these days, as Google has made the deprecation of HTTP websites a corporate priority. Those of us who have had http websites for years are forced to deal with upgrading to https, and getting a certificate that works. I had Spring Boot apps running on Amazon EC-2 instances for years, and suddenly I needed to convert them to HTTPS. But how?
Fortunately, Amazon AWS does the heavy lifting for you. You just leave your Spring Boot app running on port 80 on an EC-2 instance, and then put a load balancer in front of it to offer an encrypted https connection on port 443. You’ll have to transfer your domain name from GoDaddy (or wherever it is) to Amazon Route 53. You need to have your domain registered with Amazon so you can hook it up to the load balancer. The nice part is that Amazon will request and apply the security certificate right to the load balancer port.
The steps are:
- Get the app running on port 80 (or 8080) of on an EC-2 instance.
- Register or transfer a domain name to AWS Route 53
- Create a security group for the instance - open ports 22 and 80 (or 8080)
- Create a security group for the load balancer - open ports 80 and 443
- Configure a Target Group - link to the instance on port 80 (or 8080)
- Configure a Load Balancer - link to the Target Group and add listeners on ports 80 and 443 (when you add a listener to port 443, you’ll kick off a process to obtain a security certificate)
- Make sure, at Route 53, that the DNS names from the Hosted Zones are set in the Registered Domains section.
- Configure the Spring Boot App to run securely, and redirect HTTP to HTTPS (discussed in detail below)
- Make sure that Port 80 of the instance is custom configured to only allow access from the Load Balancer’s security group.
This tutorial from Amazon will help clarify.
Tutorial: Create a Classic Load Balancer
What is nice about this solution is that the instance runs on port 80 (or port 8080 by default) behind the load balancer. Furthermore, when setting up the load balancer, if you request port 443, Amazon will walk you through the process of obtaining a security certificate. The solution diagram will help explain.
Solution Diagram
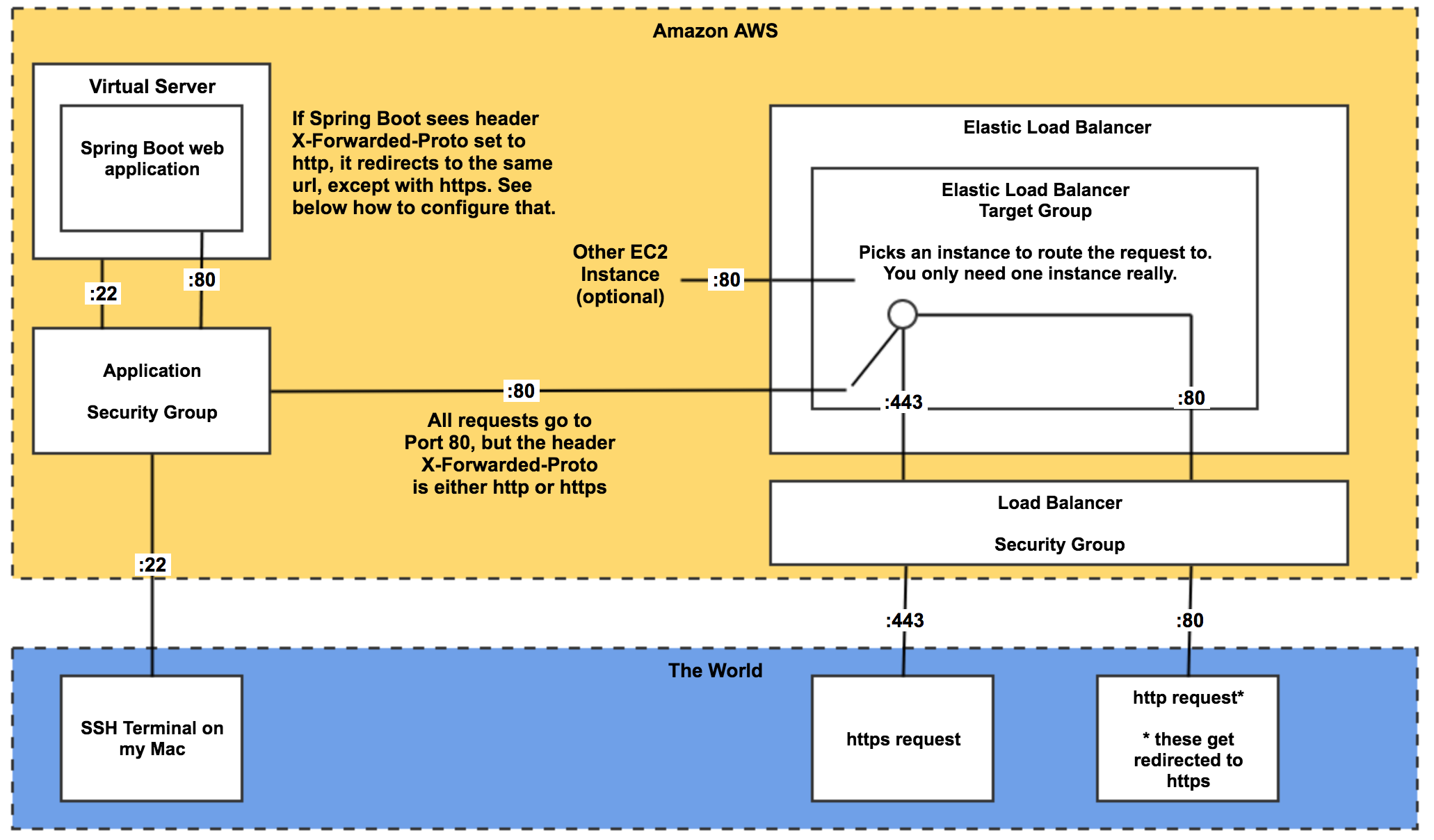
Configure the Spring Boot App to run securely, and redirect HTTP to HTTPS
After I got it all set up, I was in this state:
- http://www.mydomain.com -> stayed http BOO!
- https://www.mydomain.com -> https works YAY!
What I wanted was all requests to go to https. If someone who has never visited your site before types “www.mydomain.com” into the browser, it defaults to http unless you do something about it on your end.
I discovered that an http request that came in to port 80 of the load balancer was routed to port 80 on the instance, and a https request that came in to port 443 of the load balancer was also routed to port 80 of the instance! What I wanted my Spring Boot App to do was to detect which requests were http and reroute them to the same URL, only with https. Happily, Spring Boot can do this because the load balancer adds an extra header to the request before passing it to the EC-2 instance, called X-Forwarded-Proto. It’s value is either http or https, and with the proper configuration, Spring Boot will reroute http to https automagically!
See: Spring Boot Reference Guide - 82.3 Enable HTTPS when running behind a proxy server
Configure Spring Boot Properties
New 9/2019 - You don’t have to rely on your app to redirect http to https anymore. You can redirect the load balancer listener for port 80 to port 443 in the listener settings. You set the listener to port 443 to direct to the target group. You set the listener to port to redirect to port 443.
Add these configuration settings to the appropriate application.properties file in the resources folder.
security.require-ssl=true
server.tomcat.remote_ip_header=x-forwarded-for
server.tomcat.protocol_header=x-forwarded-proto
spring boot security class
Obviously you are using Spring Security to secure your webapp. You have to add some properties to the configuration to get http -> https redirect working. Specifically, add these settings to the HttpSecurity class.
.requiresChannel().anyRequest().requiresSecure()
Here is what the entire spring security configuration might look like:
package net.tallgeorge.homepage.security;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
public class AppSecurity extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
httpSecurity
.requiresChannel().anyRequest().requiresSecure()
.and()
.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login", "/error")
.permitAll()
.antMatchers("/")
.hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/admin")
.hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/")
.and()
.logout()
.and()
.sessionManagement()
.maximumSessions(60)
.expiredUrl("/login?expired");
}
}
Conclusion
With this configuration, if a person types www.mydomain.com or http://www.mydomain.com into the browser, they end up at https://www.mydomain.com. Even better, old links to my site still work. https links route to the identical https link. I did have to modify my Spring Boot app slightly, but it wasn’t too difficult. Good luck with your http to https conversion!